Traders have been using Candlestick chart patterns for centuries to analyse price trends and predict market reversals. Developed in Japan during the 18th century, this technique gained popularity among rice traders before finding its way into modern financial markets.
What is a Candlestick Chart Pattern?
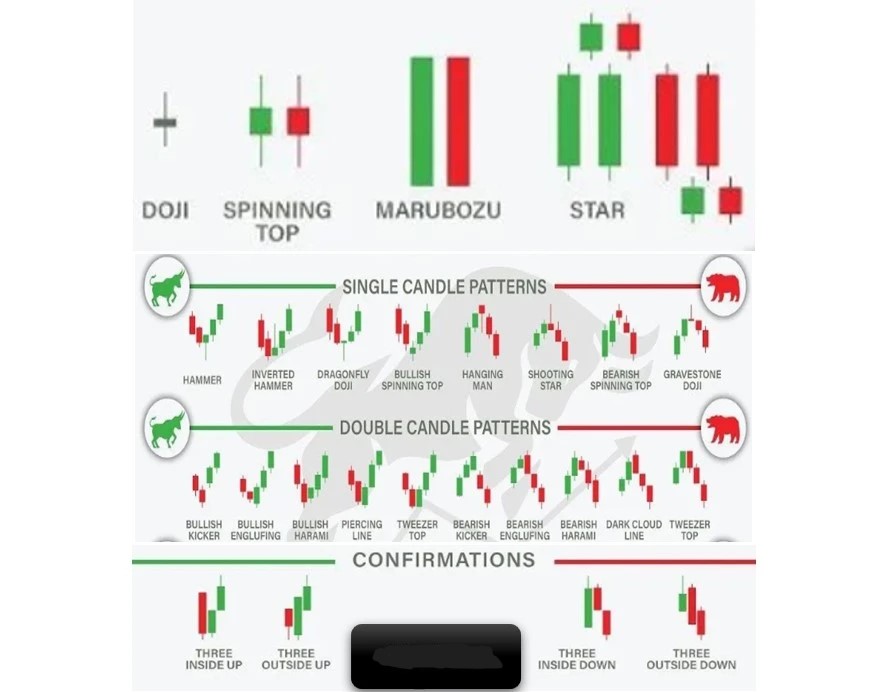
A candlestick is a candle-like shape that may have wicks on both sides or on one side only. This shape is used to graphically represent the price movements within a specific time period. Each candle visually displays the opening, closing, high, and low prices for a given interval. The body of the candle remains filled (or Red) or hollow (or Green), depending on whether the closing price is higher or lower than the opening price. The upper and lower shadows or wicks, represent the price range between the high and low of the period. These wicks tell that the price went to that point but could not sustain it there.
Understanding Candlestick Chart Components

To effectively interpret candlestick chart patterns, it is crucial to understand the key components of each candle. The body of the candle shows that the price opened at one point and closed at another. If the body of the candle is filled (or Red), it shows that the upper end of the body was the opening level and the lower end of the body was the closing level, which indicates a bearish sentiment.
You might also like : What is Swing Trading?
On the contrary, a hollow (or Green) body represents that the price opened at the lower end of the body and closed at the higher end of the body which evinces a bullish sentiment. Furthermore, you might also witness a wick above and/or below the body, which indicates that the price went up to those levels but reversed to close at a lower or upper level.
Most Common Candlestick Chart Patterns
Candlestick chart patterns can be categorized into three main types: bullish reversal patterns, bearish reversal patterns, and continuation patterns.
- A few bullish reversal candlesticks are Hammer, Bullish engulfing, and Morning Star.
- A few bearish reversal candlesticks are Shooting Star, Bearish Engulfing, and Evening Star.
- A few Continuation candlestick patterns are Doji, Rising Three Methods, and Falling Three Methods.
How to Read Candlestick Patterns?
Interpreting candlestick patterns requires a deep understanding of their formations and implications. Let’s delve into two types of candlestick patterns: single candlestick patterns and multiple candlestick patterns.
Single Candlestick Patterns
Single candlestick patterns derive their meaning from the shape and characteristics of a single candle. A few examples of such patterns are:
Doji Candlestick Pattern
A Doji occurs when the opening and closing prices are nearly equal (see the video below), indicating indecision in the market.
Hammer Candle Pattern
A hammer has a small body and a long lower shadow (see the video below), suggesting a potential trend reversal from bearish to bullish.
Shooting Star
A shooting star has a small body and a long upper shadow (see the video below), signaling a possible shift from bullish to bearish sentiment.
Multiple Candlestick Patterns
Multiple candlestick patterns consist of two or more candles and provide insights into the market sentiment over a specific period. Examples of multiple candlestick patterns are as follows:
Bullish Engulfing Pattern
A pattern is said a bullish engulfing when there is a formation of a Hollow (or Green) candle after a Filled (or Red) candle in a way that the body of the latter formed candle covers the body of the Filled (or Red) candle completely (see the video above). It means the Hollow (or Green) candle opens below the close of the Filled (or Red) candle and closes above the opening of that candle.
Bearish Engulfing Pattern
The opposite of the bullish engulfing pattern (see the video above), this formation suggests a potential bearish reversal as a large bearish candle engulfs the previous small bullish candle.
Morning Star
The morning star pattern is a three-candle formation characterized by a large bearish candle, followed by a small indecisive candle (maybe a Doji or Doji-like candle with a small body), and finally a large bullish candle (see the video above). It signifies a potential trend reversal from bearish to bullish.
Evening Star
The Evening Star pattern is just opposite to the Morning Star; a three-candle formation characterized by a large bullish candle, followed by a small indecisive candle (maybe a Doji or Doji-like candle with a small body), and finally a large bearish candle (see the video above). It signifies a potential trend reversal from bullish to bearish.
Rising-Three Methods Candlestick Pattern
It is a setup of three consecutive candles. In this, the first candlestick is a long bullish (green or hollow) candle that indicates a strong upward move. The second, third, and fourth candlesticks are relatively small and trade within the high and low range of the first candlestick. These three candles are typically bearish (red or filled), but they can also be doji candles (with small or no real body). The fifth and final candlestick is a long bullish (green or hollow) candle that breaks above the high of the first candlestick. This candle confirms the continuation of the uptrend.

Falling-Three Method
This set is just opposite to Rising-Three. In this, the first candlestick is a long bearish (red or filled) candle that indicates a strong downward move. The second, third, and fourth candlesticks are relatively small and trade within the high and low range of the first candlestick. These three candles are typically bullish (green or hollow), but they can also be doji candles (with small or no real body). The fifth and final candlestick is a long bearish (red or filled) candle that breaks below the low of the first candlestick. This candle confirms the continuation of the downtrend.

Importance of Candlestick Chart Patterns in Technical Analysis
Candlestick chart analysis play a vital role in technical analysis as they provide valuable insights into market sentiment. By understanding and correctly interpreting these patterns, traders can identify potential entry and exit points for their trades.
You might also like to read : What is Intraday Trading and How is it done?
Candlestick patterns also help traders gauge the strength of a trend, predict reversals, and confirm other technical indicators, enhancing the accuracy of their trading strategies.
Trading Strategies using Candlestick Chart Patterns
There are several strategies of trading candlestick patterns. Here are a few popular approaches:
Trend Reversal Strategy
This strategy involves identifying reversal patterns, such as the hammer or morning star, to anticipate trend reversals and enter trades in the opposite direction.
Continuation Strategy
Continuation patterns, like the rising or falling three methods, can help traders identify temporary pauses in an ongoing trend, allowing them to stay in the market until the trend resumes.
Breakout Strategy
Traders can use candlestick patterns, such as the bullish or bearish engulfing pattern, to identify potential breakouts from consolidation zones and enter trades in the direction of the breakout.
Tips for Effective Use of Candlestick Chart Patterns
To make the most of candlestick patterns, consider the following tips:
Combine with other Indicators
These patterns are most effective when used in conjunction with other technical indicators, such as moving averages or trend lines, to confirm signals and reduce false positives.
Consider the Timeframe
These patterns may vary in significance depending on the timeframe being analysed. Assess patterns on multiple timeframes to gain a comprehensive view of the market.
You might also like : What is Positional Trading?
Practice and Backtesting
Before applying candlestick patterns in live trading, practice identifying and interpreting them on historical charts. Backtesting can help validate the effectiveness of your chosen strategies.
Stay Updated
Keep abreast of market news and events that may impact price movements. Fundamental factors, such as economic reports or geopolitical developments, can influence the effectiveness of candlestick patterns.
Manage Risk
Implement proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders and adhering to position sizing principles. While candlestick patterns provide valuable insights, they are not foolproof and can result in losses if not used with proper risk controls.
Advantages and Limitations of Candlestick Chart Patterns
Candlestick patterns offer several advantages for traders:
Visual Representation
Candlestick charts provide a visually appealing and intuitive way to analyze price movements, making it easier for traders to spot potential trading opportunities.
Quick identification of market sentiment
The filled or hollow bodies of candlesticks, along with the length of shadows, allow traders to quickly assess whether the market sentiment is bullish or bearish.
Strong Historical Significance
Candlestick charting techniques have stood the test of time and have been successfully used for centuries. The historical significance of these patterns adds to their reliability.
However, it’s important to be aware of the limitations of these patterns:
Subjectivity
Interpreting candlestick patterns involves a degree of subjectivity. Traders may have different interpretations of the same pattern, which can lead to inconsistent analysis.
False Signals
Like any technical analysis tool, these patterns are not infallible and can produce false signals. It’s crucial to combine them with other forms of analysis to increase the probability of accurate predictions.
Lack of Predictive Power
While these patterns provide insights into market sentiment, they do not guarantee future price movements. They should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis for more robust decision-making.
Conclusion
Candlestick chart patterns are invaluable tools for traders and investors seeking to gain insights into market sentiment and make informed trading decisions. By understanding the various candlestick patterns, their interpretations, and their limitations, traders can enhance their technical analysis skills and increase their chances of success in the financial markets.